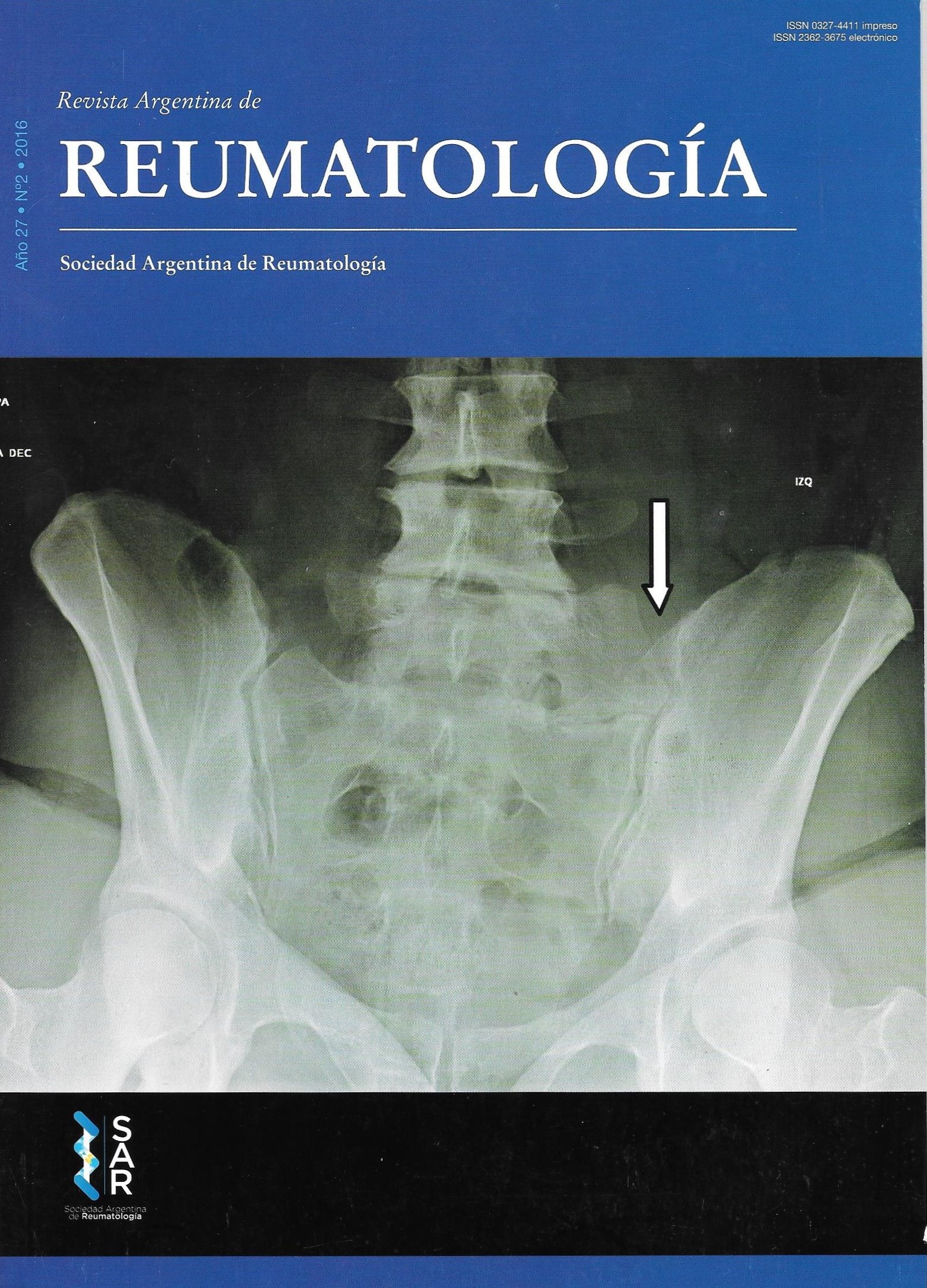
Percepción de la AR en una población fuera del ámbito sanitario
Resumen
Objetivos: El acceso temprano a la población de pacientes con artritis reumatoidea (AR) a la asistencia especializada es un predictor de buen pronóstico. Sin embargo, la demora en la consulta es una constante; fueron identificados factores tales como los vinculados al paciente, el médico generalista o al sistema de salud. El objeto del estudio fue el de explorar la percepción de la población fuera del ámbito asistencial en un escenario potencial de sintomatología compatible con AR.Citas
I. Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, O’Fallon WM. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: have we made an impact in 4 de-cades? J Rheumatol 1999;26:2529-33.
II. Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Williams CA, et al. The mortality of rheumatoid arthri-tis. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37:481-94.
III. van der Heijde DMFM. Radiographic imaging: the “gold standard” for assessment of disease progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000;39(suppl 1):9-16.
IV. Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, et al. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid ar-thritis: comparison of two cohorts who received differ-ent treatment strategies. Am J Med. 2001; 111:446-51.
V. Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, et al. Delay to institution of therapy and induction of remission us-ing single-drug or combination-disease-modifying an-tirheumatic drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:894-8.
VI. Nell VP, Machold KP, Eberl G, Stamm TA, Uffmann M, Smolen JS. Benefit of very early referral and very early therapy with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheu-matology (Oxford). 2004; 43:906-14.
VII. Finckh A, Liang MH, van Herckenrode CM, de Pablo P. Long-term impact of early treatment on radiograph-ic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 55:864- 72.
VIII. Emery P, Kvien TK, Combe B, et al. Combination etan-ercept and methotrexate provides better disease control in very early (<=4 months) versus early rheumatoid arthritis (>4 months and <2 years): post hoc analyses from the COMET study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012
IX. Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, et al. Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised tri-al. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet. 1999; 353:1568-73.
X. Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adali-mumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous metho-trexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:26-37.
XI. van der Linden MP, le Cessie S, Raza K, et al. Long-term impact of delay in assessment of patients with early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:3537-46.
XII. Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, et al. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid ar-thritis: comparison of two cohorts who received differ-ent treatment strategies. Am J Med 2001;111:446-51.
XIII. E lisa Gremese, Fausto Salaffi, Silvia Laura Bosello, Alessandro Ciapetti, Francesca Bobbio-Pallavicini, Roberto Caporali, Gianfranco Ferraccioli1 Very early rheumatoid arthritis as a predictor of remission: a mul-ticentre real life prospective study Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:858-862.
XIV. Cush JJ. Early rheumatoid arthritis—is there a window of opportunity? J Rheumatol Suppl. 2007; 80:1-7.
XV. Emery, P. Evidence Supporting the Benefit of Early Intervention in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol 2002; 29 Suppl 66: 3-8.
XVI. van der Helm-van Mil AH, le Cessie S, van Dongen H, Breedveld FC, Toes RE, Huizinga TW. A prediction rule for disease outcome in patients with recent-on-set undifferentiated arthritis: how to guide individual treatment decisions. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:433-40.
XVII. Combe B, Landewe R, Lukas C, et al. EULAR rec-ommendations for the management of early arthritis: report of a task force of the European Standing Com-mittee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:34-45.
XVIII. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classifi cation criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1580-8.
XIX. Emery P, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, et al. Early re-ferral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheuma-toid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61:290-7.
XX. Aletaha D, et al. Attitudes to early rheumatoid arthri-tis: changing patterns. Results of a survey Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:1269-1275.
XXI. Criswell LA, Such CL, Yelin EH. Differences in the use of second-line agents and prednisone for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by rheumatologists and non-rheumatologists. J Rheumatol 1997;24:2283-90.
XXII. Ward MM, Leigh JP, Fries JF. Progression of functional disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Asso-ciations with rheumatology subspecialty care. Arch In-tern Med 1993;153:2229-37.
XXIII. Nanji J, Choi M, Ferrari, R, Lyddell C, Russell A, Time to consultation and disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis--northern Alberta perspective. J Rheumatol. 2012 Apr;39(4):707-11.
XXIV. Widdifield J, Bernatsky S, Paterson JM, Thorne JC, Ci-vidino A, Pope J, Gunraj N, Bombardier C. Quality care in seniors with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis: a Canadian perspective. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Jan;63(1):53-7.
XXV. van der Linden MPM, Le Cessie S, Raza K, et al. Long term impact of delay in assessments of patient with early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62: 3537-46.
XXVI. I rvine S, Munro R, Porter D. Early referral, diag-nosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: evi-dence for changing medical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 1999;58:510-3.
XXVII. Aletaha D, Eberl G, Nell VP, Machold KP, Smolen JS. Practical progress in realisation of early diagnosis and treatment of patients with suspected rheumatoid ar-thritis: results from two matched questionnaires within three years. Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61:630-4.
XXVIII. Raza K, Stack R, Kumar K, et al. Delays in assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: variations across Europe. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:1822-5.
XXIX. Hernández-García C, Vargas E, Abásolo L, et al. Lag time between onset of symptoms and access to rheuma-tology care and DMARD therapy in a cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2000;27:2323-8.
XXX. Woolf AD, Zeidler H, Haglund U, et al. Musculoskele-tal pain in Europe: its impact and a comparison of pop-ulation and medical perceptions of treatment in eight European countries. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:342-7.
XXXI. Machold KP, Köller MD, Pfl ugbeil S, et al. The public neglect of rheumatic diseases: insights from analyses of attendees in a musculoskeletal disease awareness activ-ity. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:697-9.
XXXII. Villeneuve E, et al. A systematic literature review of strategies promoting early referral and reducing delays in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory ar-thritis Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:13-22.
XXXIII. Bell MJ, Tavares R, Guillemin F, et al. Development of a self-administered early inflammatory arthritis detec-tion tool. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2010;11:50.
XXXIV. Hwang AS, Gall V, Liang MH. Evaluation of the in-ternet for finding persons with undiagnosed rheuma-toid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Rheumatol 2009;15:218-22.
XXXV. Schulpen GJ, Vierhout WP, van der Heijde DM, et al. Joint consultation of general practitioner and rheuma-tologist: does it matter? Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:159-61.
XXXVI. Gärtner M, Fabrizii JP, Koban E, et al. Immediate ac-cess rheumatology clinic: effi ciency and outcomes. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:363-8.
XXXVII. van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Speyer I, Visser H, et al. Diagnosis and course of earlyonset arthritis: results of a special early arthritis clinic compared to routine patient care. Br J Rheumatol 1998;37:1084-8.
XXXVIII. Quinn MA, Emery P. Are early arthritis clinics neces-sary? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2005;19:1-17.
XXXIX. Deane KD, Striebich CC, Goldstein BL, et al. Iden-tification of undiagnosed inflammatory arthritis in a community health fair screen. Arthritis Rheum 2009;61:1642-9.
XL. Machold KP, Köller MD, Pfl ugbeil S, et al. The public neglect of rheumatic diseases: insights from analyses of attendees in a musculoskeletal disease awareness activ-ity. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:697-9.
XLI. Kumar K, et al. Delay in Presentation to Primary Care Physicians is the Main Reason Why Patients With
Derechos de autor 2016 Sociedad Argentina de Reumatología

Esta obra está bajo licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObrasDerivadas 4.0.